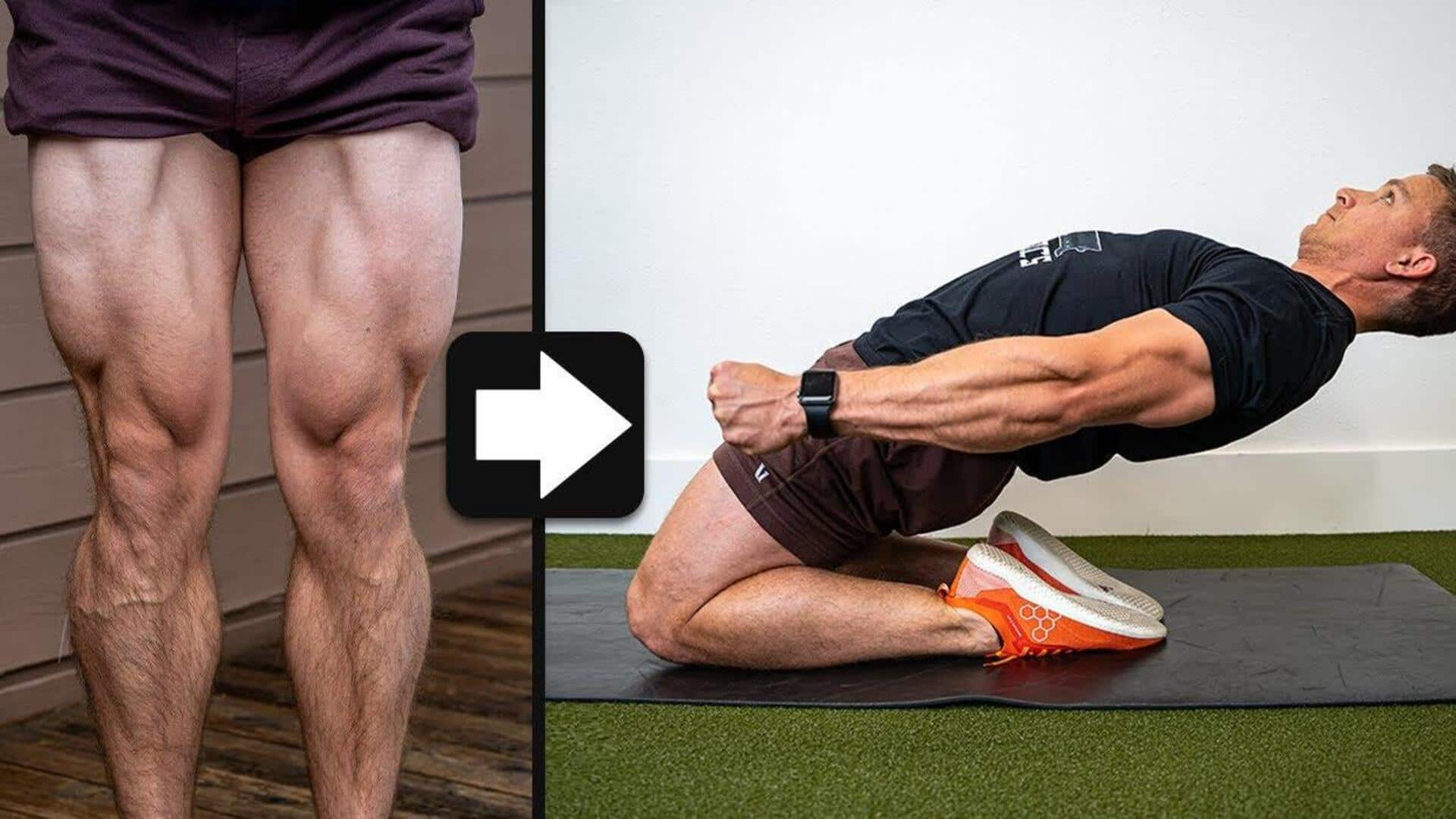
Reverse Nordic curl: How it helps improve hip health
What's the story
Reverse Nordic curls are a powerful exercise that can improve hip flexibility and strengthen the lower body. This movement, which is a variation of the traditional Nordic curl, focuses on the hip flexors, quadriceps, and glutes. By including reverse Nordic curls in your workout routine, you can improve your posture, reduce the risk of injury, and improve overall athletic performance. Here are some insights into how to perform this exercise effectively.
Tip 1
Proper form is key
Maintaining proper form is critical while performing reverse Nordic curls to avoid injuries and reap maximum benefits. Begin by kneeling on a soft surface with your knees hip-width apart. Keep your back straight as you lean backward slowly, using your core muscles for support. Ensure that your hips remain extended throughout the movement to engage the right muscles.
Tip 2
Gradual progression recommended
Like any other exercise, it's important to progress gradually with reverse Nordic curls. If you're a beginner, start by performing partial reps until you build enough strength and flexibility. As you become more comfortable with the movement, increase the range of motion gradually. This way, you can prevent strain on your joints while improving your endurance over time.
Tip 3
Consistency yields results
Consistency is key to reaping the benefits of reverse Nordic curls. Aim to incorporate this exercise into your routine at least two to three times a week for noticeable improvements in hip flexibility and lower body strength. Over time, regular practice will lead to enhanced muscle tone and better functional movement patterns.
Tip 4
Combine with other exercises
To maximize the benefits of reverse Nordic curls, combine them with other complementary exercises targeting different muscle groups. Incorporate activities like lunges, squats, or yoga stretches that focus on enhancing overall lower body strength and flexibility. This holistic approach ensures balanced muscle development while preventing overuse injuries from repetitive motions.