#TechBytes: How to get started on Linux terminal commands
What's the story
The Linux terminal is a powerful tool for anyone looking to navigate and manage their system efficiently. While it may seem intimidating at first, mastering basic commands can significantly enhance your productivity. This article provides a beginner-friendly guide to essential Linux terminal commands that will help you perform everyday tasks with ease. Whether you're managing files or monitoring system performance, these commands are fundamental to getting things done in the Linux environment.
Tip 1
Navigating the file system
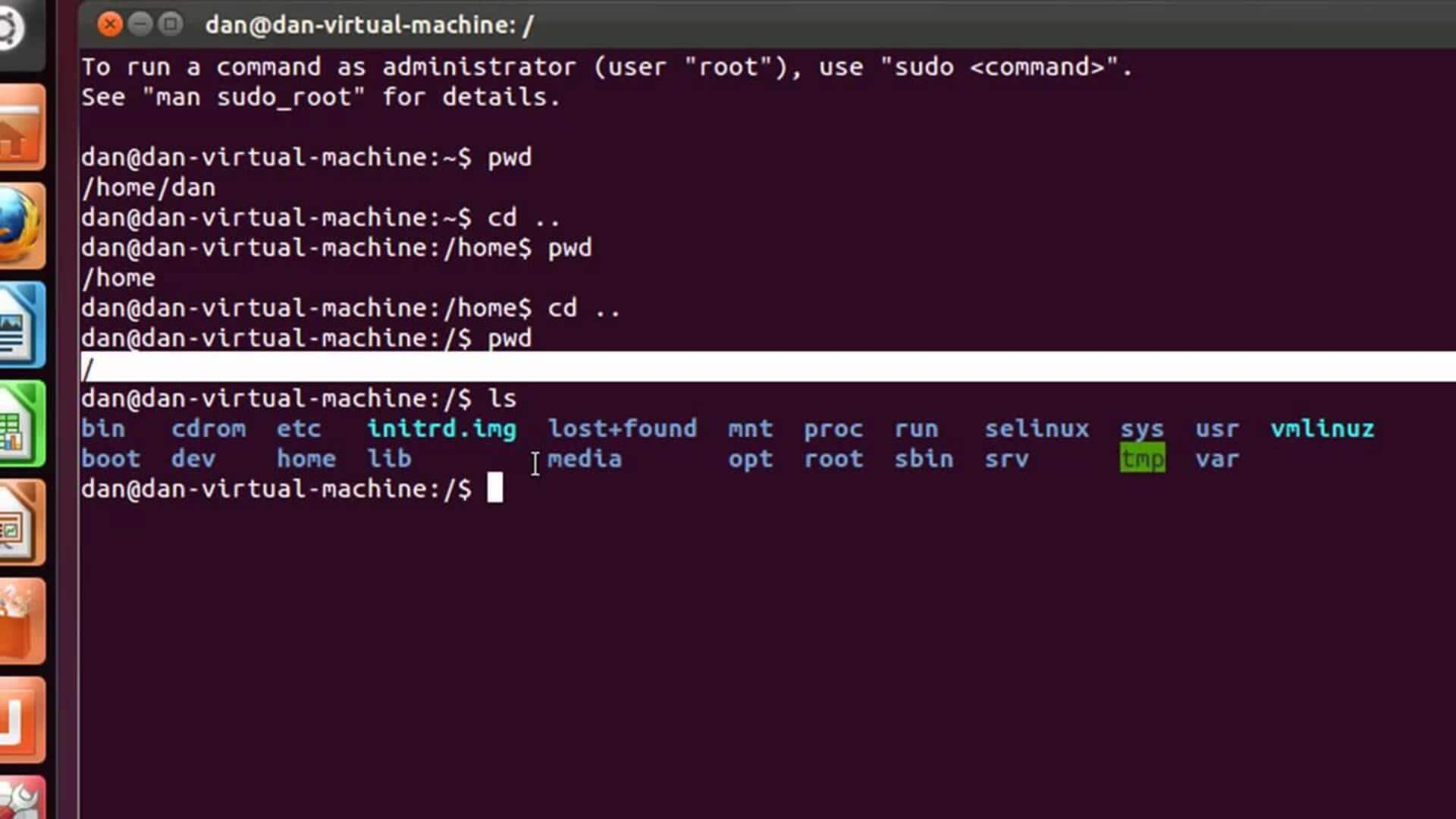
Navigating through directories is a basic skill in the Linux terminal. The command 'cd' (change directory) lets you move between directories. Use 'ls' to list files and directories in the current directory. If you want to go back to the home directory quickly, use 'cd ~'. To go up one level in the directory tree, use 'cd ..'.
Tip 2
Managing files and directories
Creating and deleting files/directories is easy with commands like 'mkdir' for making directories and 'touch' for creating empty files. To delete a file, use 'rm', while 'rmdir' removes empty directories. For renaming or moving files, use 'mv'. Always double-check before using these commands, as they can permanently delete data without confirmation.
Tip 3
Viewing file contents
To view contents of text files directly in the terminal, commands like 'cat', 'less', and 'more' come handy. 'cat' displays entire content at once, while 'less' and 'more' allow you to scroll through larger files page by page. Use these commands when you need to quickly check or read through file contents without opening an editor.
Tip 4
Monitoring system performance
Monitoring system performance is key to maintaining its health. The 'top' command provides a real-time view of processes running on your system, along with their resource usage stats like CPU and memory consumption rates. For checking disk space usage, 'df -h' offers a clear overview of available storage across all mounted filesystems.
Tip 5
Searching for files and text within files
Finding specific files or text within them can be easily done using commands like 'find' or 'grep'. While 'find' helps locate files based on criteria like name or size, 'grep' searches through file contents for specific patterns or keywords. These tools are invaluable when dealing with large amounts of data where manual searching would be impractical.