This AI-driven humanoid robot can assist in elderly care
What's the story
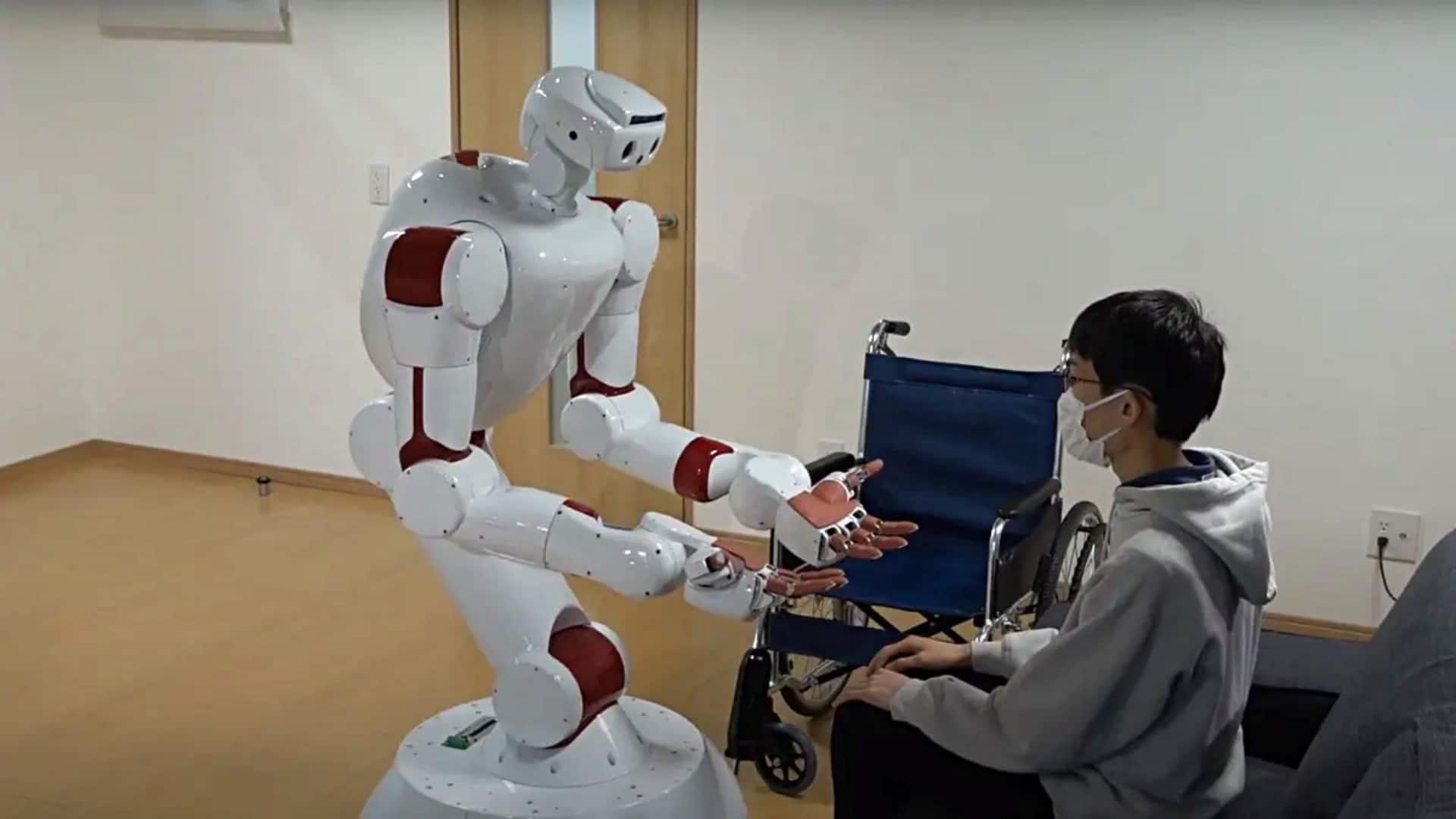
Japan is now testing a humanoid robot, called AIREC (AI-driven Robot for Embrace and Care), to assist in elderly care. The 149kg bot recently demonstrated its capabilities by gently rolling a man on his side, an important move for changing diapers or preventing bedsores. The innovation comes amid Japan's severe shortage of aged care workers and gives a glimpse into the future of robotic caregiving.
Robotic support
AIREC's role in Japan's aging society
Shigeki Sugano, a Waseda University professor leading the AIREC project, stressed the need for robotic support in Japan's fast-aging society. "Given our highly advanced aging society and declining births, we will be needing robots' support for medical and elderly care, and in our daily lives," he said. This highlights how robots like AIREC could play a role in tackling demographic challenges.
International trend
Global shift toward robotic caregiving
Globally, the trend is moving toward integrating humanoid robots and AI into elderly care. In January, China had detailed plans to integrate these technologies into their elderly care system. This shift is driven by aging populations and low birth rates, which increase the demand for care services. The transition from young to old has resulted in a decrease in nurses, emphasizing the need for automated solutions like AIREC.
Tech hurdles
Technological challenges in robotic caregiving
Despite the increasing demand for robotic caregivers, researchers at Waseda University have emphasized that the use of robotics in caregiving is still restricted due to technological hurdles. These challenges need to be addressed before such tech can be widely adopted. The researchers are working on creating DNN-powered, multipurpose, AI-driven household robots that can adjust their movements to different unforeseen scenarios.
Motion adaptability
The need for adaptive motion in caregiving robots
Adaptive motion is a critical feature for caregiving robots. Unlike industrial robots with preset movements, caregiving robots must adjust their actions to suit a range of unexpected situations. This is because the complex tasks involved in providing care require more intricate force control than directing robotic arms in precise tasks. The robot must know when and how to apply force safely and efficiently while avoiding unnecessary pressure on sensitive areas.
Innovative strategy
Waseda University's approach to robotic caregiving
In 2024, a Waseda University team proposed a deep-learning-based structure for a humanoid robot capable of dynamically adjusting joint stiffness. The strategy is based on impedance control-based direct teaching, allowing the robot to apply appropriate force without excessive pressure on unintended areas. This way, the robot can independently transition between different interaction force regimes, aided by an attention system for joint states.
Testing phase
AIREC's testing and future prospects
AIREC is still in the testing phase, but the team estimates it would be ready for nursing care or medical facilities by 2030. The initial cost of the robot would be around ¥10 million ($67,000). This timeline and pricing info gives a realistic outlook on when and how this innovative technology could become an integral part of elderly care services in Japan.